
Designing a restroom that adheres to the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) is much more than a mere compliance issue; it is about creating an environment that is inclusive and accessible for all. With specific ADA bathroom requirements guiding the layout, from the width of an aisle for wheelchair users to the installation height of a urinal, architects and builders must meticulously plan each detail. Furthermore, factors like the placement of plumbing fixtures and the integration of Braille signage require thoughtful consideration to ensure functionality and independence for users with diverse needs. In this article, readers will discover the key to successfully executing ADA restroom layouts, paving the way to create facilities that are not only legally compliant but also welcoming and practical for individuals with disabilities.
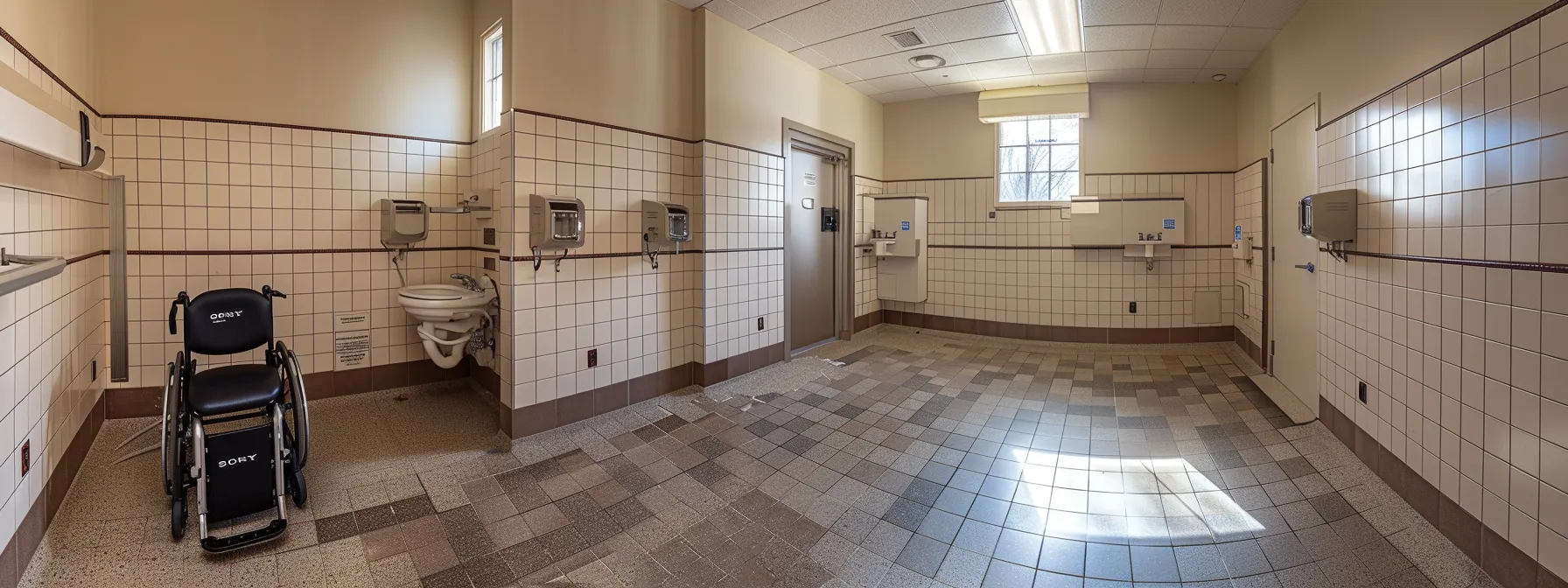

Designing restrooms that cater to the diverse needs of users involves more than aesthetic choices; it requires strict adherence to the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). This ensures usability for individuals with mobility impairments, particularly those using wheelchairs. A bathroom space must not only accommodate the physical presence of a wheelchair but also allow for the comfortable and safe execution of tasks. Understanding ADA minimum space requirements is pivotal for architects and designers. Identifying key ADA compliance criteria, thus, becomes an indispensable part of the design process. Incorporating these standards from the start not only streamlines the development workflow but also avoids costly retrofits, ensuring that all bathroom facilities are reliably ada compliant, from the placement of toilet paper dispensers to the maneuvering space around fixtures.
Ensuring that a public toilet meets the stringent criteria set forth in the ada bathroom requirements guidelines involves a thorough analysis of building code stipulations, particularly those dictating minimum space allowances. These guidelines, which are readily accessible as a pdf document for reference, emphasize the necessity of a layout that allows unobstructed mobility for individuals with disabilities, notably in the approach to fixtures, turning radius, and transitions from areas like stairs to level flooring, as well as the strategic placement of water access points.
Compliance with the American Disabilities Act hinges on precise details that cater to hand dexterity and knee space for users, which affect components such as faucet handles and under-sink clearances. Designers must be vigilant and implement a floor plan that features an adequate turning diameter for wheelchairs, often a minimum of sixty inches, to ensure users can navigate comfortably. The selection of elevators within multi-story buildings is also subject to rigorous ADA standards to facilitate unhindered access to restroom facilities on all levels.
In the initial stages of restroom design, integrating ADA compliance is imperative to foster an environment that is accessible for all individuals. Careful planning ensures that elements such as mirror reflections and menu signage maintain their visibility at heights within easy reach for seated users. Proactive incorporation of ADA standards through tools such as javascript simulations helps to visualize the allocation of room for mobility devices, preempting any design oversights.
| Design Feature | ADA Requirement | Design Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Mirror | Placement at optimal height for seated and standing users | Mounted at designated heights to reflect the image of a seated individual |
| Menu Signage | Readable font size and accessible height for all | Signage installed within line of sight from a seated or standing position |
| Room for Maneuvering | Enough space for a minimum 60-inch turning radius | Spacious floor area designed to accommodate turning wheelchairs |
| Javascript Simulation | Use of technology to ensure practical space utilization | Interactive models to assess and adjust spatial design for ADA compliance |
Transitioning from the broad principles of ADA-compliant restroom design, the focus now sharpens to the core elements that ensure compliance. This segment delves into the essential components that render restrooms accessible and functional for all individuals.
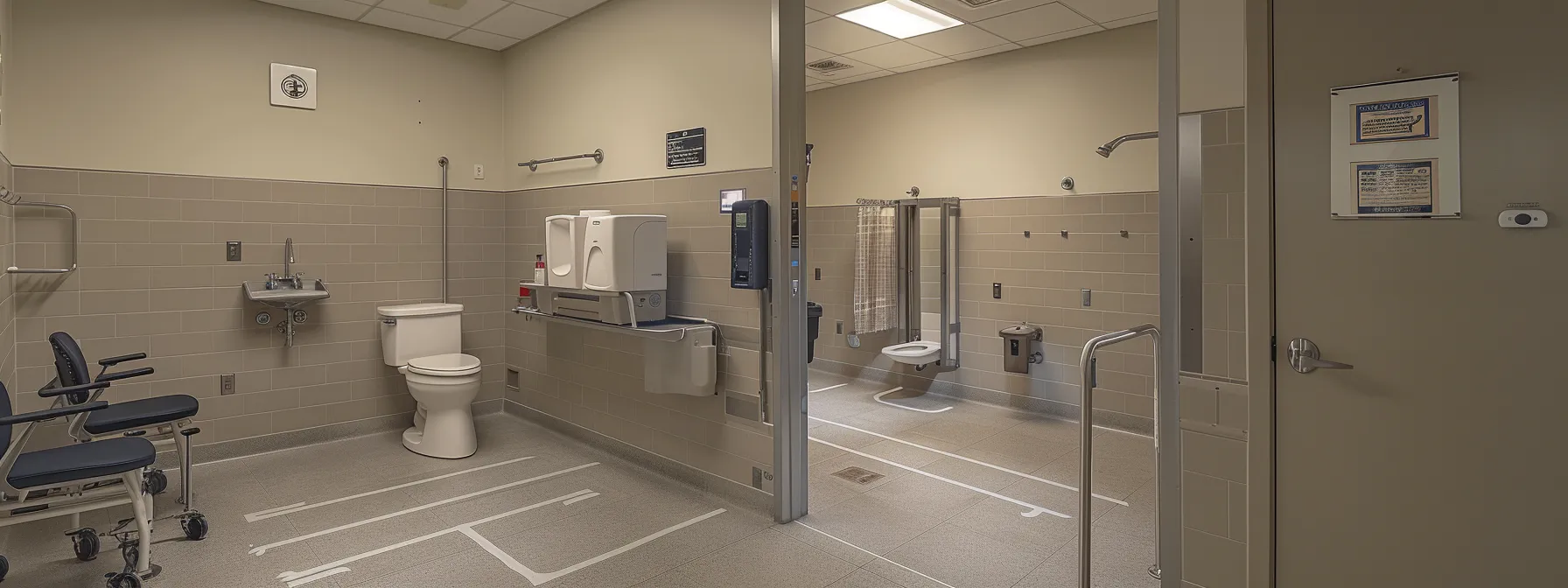

As designers delve into the specifics of crafting accessible restrooms, attention to the foundational elements outlined in the ADA is critical. The required clear floor space must accommodate wheelchair maneuverability, catering to users who require accessible parking adjacent to the facility. This consideration is complemented by explicit minimum dimensions for accessible toilet compartments, ensuring privacy and ease of use. Essential fixtures within these spaces, including water closets and lavatories, must meet the indicated proportions to facilitate usage for all. These fixtures, down to the placement of soap dispensaries, are integral to delivering a truly accessible bathroom environment, and compliance information is often found at source materials available via https. Striking a balance between these design elements paves the way for restroom facilities that uphold dignity and independence for every individual.
Designing restrooms in accordance with ADA standards necessitates a clear understanding of space requirements that allow for the full arc of a wheelchair‘s movement. The international building code specifies that sufficient toe and knee clearance around the toilet seat is essential, ensuring that individuals in wheelchairs can approach, transfer, and use the facilities with independence and ease. The length and width of the clear floor space must be meticulously calculated to meet ada compliance, fostering an environment of inclusivity.
ADA standards require that toilet compartments provide sufficient space to ensure easy navigation and usability for individuals with disabilities. The space must comfortably accommodate a wheelchair, and design specifications in the ADA document stipulate that, in addition to the main area, ancillary accommodations such as sinks and showers maintain proper distance and positioning relative to the toilet. Furthermore, the placement of grab bars must be precise to aid in safe transfers, underpinning the importance of meticulous space planning in restroom designs.
In restrooms designed to be accessible for patients, adherence to ADA standards is reflected in the required features for water closets and lavatories. Such elements include the height and location of the soap dispenser to be reachable for all users, especially those seated in wheelchairs, and adequately sized toilet compartments that allow for unimpeded access and transfer, emphasized by supportive surrounding wall grab bars.
Ensuring restrooms meet ADA requirements sets the foundation. Next, attention turns to creating wheelchair accessible toilet compartments that exceed standards and expectations.
In the realm of restroom design, laying out toilet compartments to accommodate wheelchairs is more than a gesture towards inclusivity; it’s a commitment to ensuring accessibility for all users. Detailing the layout specifications for wheelchair accessibility demands a comprehensive understanding of the dimensions and arrangements that enhance user autonomy while complying with legal standards. Meticulous design strategizing addresses how each closet space grants ease of entry, sufficient internal circulation, and the incorporation of key elements like grab bars. Relevant information on minimum space requirements comes into play, delineating the necessary proportions to navigate and operate within the confines of a restroom space that also meets the practical need to maneuver past potential obstacles such as curbs. Addressing these facets with precision in each design ensures that restrooms support the functional requirements of every individual.
In the construction of restrooms adhering to ADA standards, the layout must allocate a parking space specifically for wheelchairs within the accessible toilet compartment. The design should ensure doorways facilitate unimpeded entry and exit, reinforcing the space‘s utility and safety for individuals with disabilities.
Each restroom layout must fulfill ADA criteria by providing adequate dimensions that ensure full functionality: key measurements must include a 60-inch turning space for wheelchairs, positioning of the toilet paper dispenser within arm’s reach without the need to manoeuvre, and the incorporation of access points for plumbing fixtures without impeding the compartment’s use. A carefully structured table of contents within ADA guidelines concisely details the necessary dimensions and clearances around fixtures to guide the design process.
Design marvels in wheelchair–accessible stalls set the stage; optimal placement of lavatories and sinks perfects the function. Accessibility transforms into seamless convenience as attention turns to the strategic positioning of these essential fixtures.
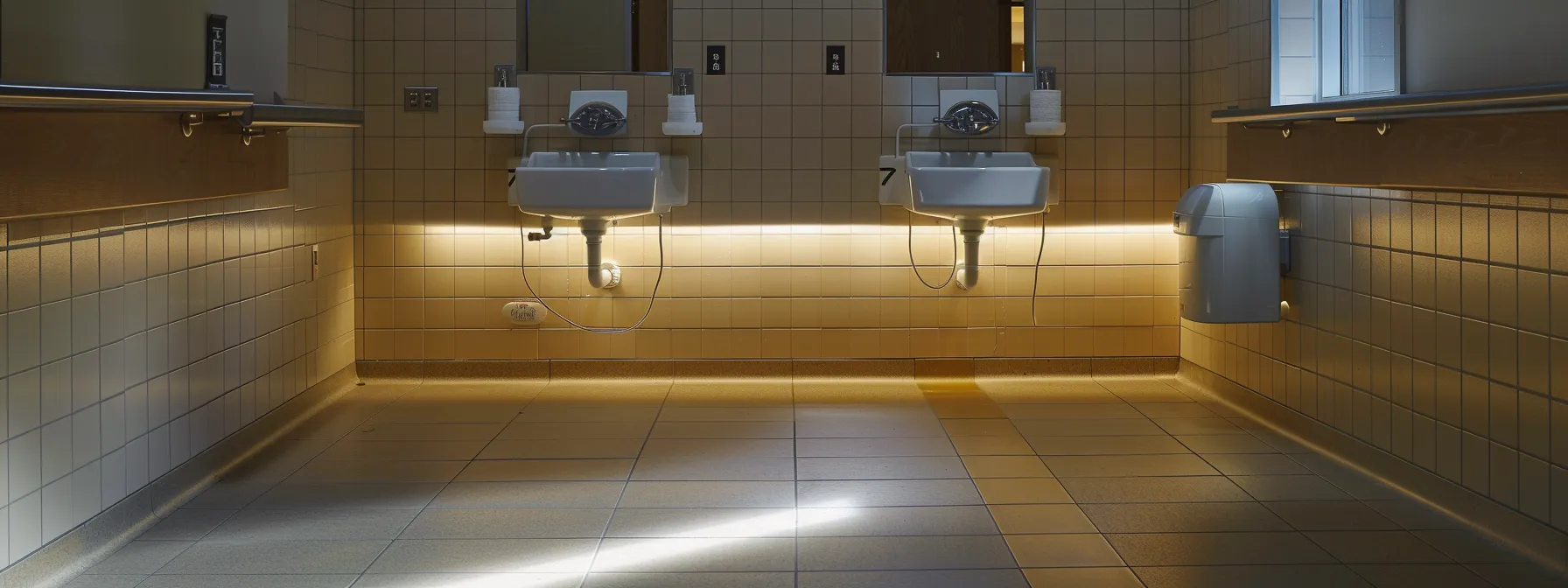

Addressing proper lavatory and sink placement in restroom layouts holds significant weight under the law, as it adheres to the Americans with Disabilities Act’s strict regulations on height and clearance requirements. Design elements must be strategically configured to allow for easy access to paper towels, hand dryers, and other amenities, ensuring individuals with disabilities can use the facilities with independence. Properly mounted faucets, with valves that are manageable for all users, and other accessories at optimal heights further ensure sufficient access and usability. These considerations are critical in fostering an inclusive environment, where every detail from the placement of towel dispensers to the operation of a hand dryer, enriches the user experience and adheres to ADA compliance.
In constructing accessible restrooms, it is essential to observe strict height and clearance requirements for lavatories and sinks, ensuring seamless use for all individuals. The regulations stipulate that facilities within a unisex or gender-specific restroom must have sinks installed at a height that allows user access from a seated position, with sufficient knee and toe clearance beneath the sink‘s apron. These criteria are vital, particularly concerning the floor space designated for safe and unobstructed wheelchair maneuverability:
| Design Feature | Height Standard | Clearance Requirement | Impact on User |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sink Installation | Must be accessible from a seated position | Adequate knee and toe clearance beneath sink apron | Allows for comfortable and independent use by wheelchair users |
| Floor Space | N/A | Sufficient unobstructed space for wheelchair maneuverability | Ensures safety and ease of movement within the restroom |
To secure a restroom environment that is accessible and practical for all users, careful positioning of lavatories and sinks is paramount. Considerations must include not only the adequate height for wheelchair accessibility but also the unobstructed approach for individuals with differing mobility needs, bolstering the safety and autonomy of each user in a diverse population.
Proper layout is just the beginning; safety features are next on the agenda. Let’s tackle the vital role of grab bars and handrails for accessibility and security.

Within the parameters established for ADA-compliant restroom designs, the placement and specifications of grab bars and handrails emerge as crucial elements for ensuring the safety and support of all users. These components are not merely additional features; they serve as fundamental fixtures, pivotal in enabling individuals with various mobility challenges to navigate the space securely. Both the precise positioning and the critical dimensions of grab bars directly influence the restroom’s usability, providing indispensable stability for users as they transfer to and from wheelchairs or move about the facility. Designers tasked with creating accessible restrooms are obliged to adhere to exacting standards, which dictate the height, length, and location of these assistive devices to foster an environment that upholds the autonomy and safety of those reliant on the enhanced support they offer.
Adherence to ADA guidelines dictates that grab bars and handrails must be installed with meticulous attention to position and size: their height must be within the range of 33 to 36 inches above the floor, with dimensions that allow for a secure grip and support during transfers. This precise installation is crucial for restroom accessibility, as it directly affects safety and user confidence.
The strategic placement of grab bars significantly enhances the functionality of an ADA-compliant restroom by empowering users with additional support and steadiness. Correctly positioned grab bars around toilets and within shower stalls enable individuals to maintain balance and independence while performing necessary tasks, thereby improving the usability and safety of the restroom facilities for individuals with disabilities.
Addressing the placement of grab bars and handrails paves the way for a finer point of focus: dispenser location. Mastering this aspect is vital for restroom accessibility compliance, fostering a seamless restroom experience for all users.

Within the meticulous design of ADA compliant restrooms, the placement of dispensers for toilet tissue, soap, and towels emerges as a nuanced aspect that requires specific oversight. Designers must ensure these vital amenities adhere to predefined standards that guarantee their accessibility to all users, particularly those with physical impairments. While prioritizing accessibility, attention must also be given to the overall practicality of restroom layouts, ensuring that the arrangement of these dispensers enhances, rather than impedes, the utility and efficiency of the space. The balance struck between adherence to code and the optimization of available space defines the success of a restroom’s functionality for its diverse users.
In ADA-compliant restrooms, dispensers for toilet tissue, soap, and hand towels must be located within reach for individuals seated on a wheelchair, without requiring them to strain or rotate excessively: they must be mounted no higher than 40 inches above the floor. The design must provide proximity and ease of access, placing these essential dispensers at appropriate heights and positions to serve all users, including those with reduced range of motion.
| Dispenser Type | Maximum Height | Location Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Toilet Tissue Dispenser | Not above 40 inches from the floor | Forward or side reach must be unobstructed |
| Soap Dispenser | Not above 40 inches from the floor | Accessible from a front approach |
| Hand Towel Dispenser | Not above 40 inches from the floor | Reachable from a seated position without the need to move |
In crafting ADA-compliant restrooms, designers must consider the synergy between accessibility and spatial harmony. The strategic positioning of dispensers aligns with regulatory compliance while preserving the restroom’s intuitive flow, allowing individuals with disabilities to navigate and utilize the space with autonomy and dignity.
| Dispenser Type | Height Restriction | Placement Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Paper Towel | Not exceeding 48 inches | Near hand washing stations, facilitating reach without maneuvering |
| Soap | Within 44 inches | Adjacent to sinks, accessible directly from the front |
| Sanitary Napkin | Below 40 inches | Installed inside stalls, within easy arm’s reach while seated |
Mastering ADA restroom layout standards is essential to guarantee that public facilities provide safe, accessible environments for individuals with disabilities. Adherence to minimum space requirements ensures vital maneuverability and the seamless use of fixtures for wheelchair users. By integrating ADA guidelines into the design process, architects create restrooms that offer independence and maintain the dignity of all users. Ultimately, well-designed ADA-compliant restrooms reflect a commitment to inclusivity and the legal mandate of accommodating diverse populations.

As a business owner, you have a responsibility to ensure that your business complies with the Americans with Disabilities Act(ADA). Not only is it a

When making renovations, there are many things you need to consider, from the structure to the aesthetics of the building. However, one major aspect that